#trigger Azure devops pull request trigger
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Automating Deployments with GitHub Actions and Terraform

Automating Deployments with GitHub Actions and Terraform When it comes to deploying infrastructure or applications, manual processes can be time-consuming and error-prone.
Automating these deployments with tools like GitHub Actions and Terraform can significantly improve efficiency, consistency, and reliability in your workflows.
Here’s an explanation of how these two tools work together and why they’re a great combination for modern DevOps pipelines.
What is GitHub Actions?
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) platform built into GitHub.
It allows you to automate workflows by defining them in YAML files stored in your repository.
Workflows can be triggered by specific events, like pushing code to a branch, opening pull requests, or even on a schedule.
Why use GitHub Actions?
Fully integrated with GitHub repositories. Supports multiple programming languages and environments.
Customizable workflows for different stages (build, test, deploy). Marketplace for pre-built actions to simplify your pipelines.
What is Terraform? Terraform is an Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that allows you to define and provision cloud infrastructure using a declarative configuration language.
It supports multiple providers (AWS, Azure, GCP, and more), making it a versatile solution for managing infrastructure.
Why use Terraform?
Consistent and reproducible infrastructure. Code-driven approach for scalability and documentation.
State management to track infrastructure changes. Provider-agnostic for multi-cloud strategies.
How They Work Together Combining GitHub Actions and Terraform creates a seamless pipeline for infrastructure deployment and updates.
Here’s how it typically works:
Code Changes:
You define your infrastructure as code in Terraform configuration files and store them in a GitHub repository.
Trigger Workflow:
A GitHub Action is triggered whenever a specific event occurs (e.g., a new push to the main branch or merging a pull request).
Plan and Validate:
The workflow uses Terraform to validate and generate a plan for infrastructure changes.
This ensures there are no syntax errors or unexpected modifications.
Apply Changes: After approval (if needed), the workflow applies the Terraform plan to deploy or update the infrastructure.
Feedback:
The pipeline provides feedback on deployment status, either success or failure, through GitHub.
Setting It Up Here’s a simple workflow to automate Terraform deployments with GitHub Actions:
Key Benefits Scalability: Manage infrastructure for projects of any size without manual intervention.
Efficiency: Reduce deployment time and eliminate repetitive tasks.
Consistency:
Ensure all environments are deployed using the same code and processes.
Security:
Use GitHub Secrets to store sensitive data like API keys and access tokens.
Best Practices Use GitHub Secrets:
Store sensitive variables securely.
Plan Before Apply:
Always review the Terraform plan before applying changes. Modularize
Terraform Code:
Break your Terraform configurations into reusable modules for better organization. Enable Notifications:
Configure GitHub Actions to send notifications (e.g., Slack, email) about deployment status.
By leveraging GitHub Actions and Terraform together, you can automate and streamline your deployment processes, giving your team more time to focus on building great products.
Add this automation to your DevOps toolkit to simplify infrastructure management and improve productivity.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/devops-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
Integrating Web UI Testing with CI/CD Pipelines: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction to CI/CD and Web UI Testing
Begin by explaining Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines and their role in modern software development. Highlight the importance of integrating web UI testing into these pipelines for faster delivery and consistent quality.
Benefits of Integration
Discuss advantages such as automated regression testing, early defect detection, and seamless deployment workflows.
Step 1: Choose the Right Tools
Explain how to select tools for both CI/CD (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps) and UI automation testing (e.g., Selenium, Playwright, Cypress) that fit your tech stack.
Step 2: Create Robust Automated Test Scripts
Highlight the importance of building reliable and reusable UI test scripts that cover critical functionalities and user flows.
Step 3: Configure Your CI/CD Pipeline
Detail the process of adding a test stage to the CI/CD pipeline. Include triggering tests automatically on code commits or pull requests.
Step 4: Enable Parallel Testing
Discuss how to speed up the testing process by running tests in parallel across different browsers and devices.
Step 5: Monitor and Report Results
Explain how to generate reports and notifications for failed tests, ensuring rapid feedback for the development team.
Conclusion
Reiterate the importance of integrating web UI testing into CI/CD pipelines to achieve faster, more reliable software releases.
#web automation testing#ui automation testing#web ui testing#ui testing in software testing#automated website testing#web automation tool#web ui automation#ui automation tool#web automation software#automated testing web applications#automated web ui testing#web app testing
0 notes
Text
Essential Azure DevOps Skills: What You Need to Succeed in Modern Software Development

In today's fast-paced software development landscape, tools that support automation, collaboration, and streamlined deployment have become essential. Azure DevOps, a comprehensive set of development tools and services by Microsoft, has emerged as a leading platform to support DevOps practices throughout the software development lifecycle.
To effectively use Microsoft Azure course DevOps, professionals need a well-rounded set of skills that go beyond just coding. From managing version control to setting up deployment pipelines, these skills are crucial for building modern, scalable, and reliable software systems.
In this article, we’ll explore the key Azure DevOps skills you need to master to boost your productivity, improve collaboration, and deliver software efficiently and securely.
What Are Azure DevOps Skills?
Azure DevOps skills refer to the technical competencies, best practices, and practical knowledge required to use Azure DevOps tools effectively. These include skills related to:
Source control and version management
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Azure cloud services integration
Automation and monitoring
Whether you’re a developer, DevOps engineer, system administrator, or project manager, mastering these skills can significantly improve your ability to manage software delivery from start to finish.
1. Source Control Management
One of the foundational skills in Azure DevOps is managing source code using a version control system. Azure DevOps supports Git repositories through Azure Repos, providing teams with tools to collaborate on code effectively.
Key Skills to Learn:
Understanding Version Control Concepts: Learn how version control systems work, why they are essential, and the difference between centralized and distributed systems.
Proficiency in Git: Git is the most widely used version control system. You should be comfortable with basic Git operations like clone, commit, push, and merge.
Branching Strategies: Master different branching models such as Git Flow, trunk-based development, or feature branching to manage code changes in a structured way.
Pull Requests and Code Reviews: Know how to create and manage pull requests, conduct code reviews, and resolve merge conflicts.
2. Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous Integration (CI) is a critical DevOps practice where developers regularly merge code changes into a shared repository, followed by automated builds and tests.
Key Skills to Learn:
Creating CI Pipelines: Use Azure Pipelines to set up CI workflows that automatically build and validate code after each commit.
Writing Build Scripts: Learn how to write and configure build scripts using YAML or visual editors within Azure Pipelines.
Automated Testing Integration: Integrate testing frameworks (like NUnit, JUnit, or PyTest) into your CI pipelines to ensure that new code doesn’t break existing functionality.
CI helps catch issues early in the development process, improving code quality and reducing bugs in later stages.
3. Continuous Delivery (CD)
While CI focuses on automatically building and testing code, Continuous Delivery (CD) takes it a step further by automating the deployment process.
Key Skills to Learn:
Configuring CD Pipelines: Set up CD pipelines in Azure Pipelines to deploy your applications automatically to various environments like development, staging, and production.
Deployment Strategies: Understand different deployment strategies such as blue-green deployments, rolling updates, and canary releases to minimize downtime and risk.
Managing Triggers and Approvals: Configure automatic or manual triggers and approval gates to control when and how deployments occur.
4. Azure Services Integration
Azure DevOps is designed to work seamlessly with various Azure cloud services. Understanding how to integrate these services into your DevOps pipelines is essential for modern application delivery.
Key Skills to Learn:
Deploying to Azure App Services: Learn how to deploy web applications directly to Azure App Service using Azure Pipelines.
Using Azure Functions: Automate workflows or deploy serverless functions as part of your CI/CD process.
Managing Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Deploy and manage containerized applications in AKS, Microsoft’s managed Kubernetes offering.
ARM Templates for Resource Management: Define and manage your cloud infrastructure using Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates.
5. Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code is a critical part of DevOps practices. It allows you to define your infrastructure using code, making deployments repeatable, scalable, and easy to manage.
Key Skills to Learn:
Using ARM Templates: ARM templates allow you to describe your Azure resources in JSON format and automate their deployment.
Working with Terraform: Terraform is a popular tool for defining infrastructure across multiple cloud platforms, including Azure. Learn its syntax (HCL) and how to write reusable, version-controlled infrastructure modules.
Automation and Scaling: Automate the provisioning, updating, and decommissioning of infrastructure using scripts and configuration files.
Why These Skills Matter in a DevOps Career
Organizations are rapidly adopting DevOps to improve software quality, reduce release cycles, and increase agility. Azure DevOps brings all necessary tools into one platform, but to use it effectively, professionals need a combination of development, operational, and automation skills.
Here’s how mastering Azure DevOps skills helps you:
Better Collaboration: Facilitates smoother communication between development and operations teams.
Higher Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks and reduces time spent on manual processes.
Improved Quality: Encourages continuous testing and monitoring, leading to more stable releases.
Career Growth: Azure DevOps expertise is in high demand, especially in organizations moving to the cloud or adopting DevOps practices.
Conclusion
Azure DevOps is more than just a set of tools—it's a platform that supports modern software development practices through automation, collaboration, and integration with the cloud. To take full advantage of Azure DevOps, professionals must develop skills in source control, CI/CD, infrastructure automation, and Azure services.
If you're just starting out, consider hands-on learning through projects, online courses, or Azure DevOps certification programs. With consistent effort, you'll gain the practical expertise needed to manage the full software development lifecycle using Azure DevOps.
0 notes
Text
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger Azure devops pull request trigger Headlines today Azure devops pull request trigger Deploy pull request Artifacts with Azure Pipelines Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2020 | Azure DevOps Server 2019 Pull requests provide an effective way to have code reviewed before it is merged to the codebase. However, certain issues can be tricky to find until the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Download GitKraken crack (keygen) latest version 9VU3#

💾 ►►► DOWNLOAD FILE 🔥🔥🔥 Git is what gives a dev their power…It binds the galaxy together. Workspaces can currently support up to repositories for an Azure Project. Users can type either gk rebase -i or gk rebase —interactive along with two refs to open the interactive rebase view. If only one ref is passed it will perform the rebase of the branch currently checked out onto the specified ref. Bug Fixes: Bugs…You will never find a more wretched hive of scum and villainy. Users will see increased performance when opening a commit diff for very large images. Large images will now display as a binary file Instead of producing an error. For large files, such as images and other media, we recommend using Git LFS. Dotted graph lines will no longer take precedence when overlapping with solid lines in graph views. When un-hiding a remote, users can continue hiding or un-hiding remotes without waiting for the triggered automatic fetch to resolve. Azure DevOps integrations and all self hosted integrations will now work properly on our new Teams license tier. Users can now use quotation marks when naming Workspaces. All Organization and Team actions will remain available after using the login screen. The scrollbar in the GitKraken Terminal will now remain clickable in all situations. When a user pushes many files up at once to GitHub, they will no longer experience an OAuth infinite loop. Opening repositories via gitkraken —path when GitKraken is already open will now work as expected. Improvements: An elegant Git client for a more civilized age. Note: Significant work towards reducing checkout times for LFS repos is underway and we plan to include these improvements in the GitKraken Client v8. When creating a new Team, members can now be added as part of the creation process. Team members are now sorted by username in the Teams section, found in the left panel of GitKraken Client. Improvements to GitKraken Workspaces: Workspaces can now be shared as Team Workspaces, allowing users to share the Workspace with specific teams within their Organization. In the Workspaces Repository view, clicking on the name of a repository will open it in a Repo Tab. Users can view repository information by clicking on the Open Repository Details option, found on the right side of the Repositories view. Users will find more options for filtering in the Workspaces Pull Requests view. For Windows users, GitKraken Client will now respect the core. On Windows, core. GitKraken CLI autocomplete will now be able to suggest more than one argument in these commands: git add.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Download GitKraken crack (license key) latest version 89T*

💾 ►►► DOWNLOAD FILE 🔥🔥🔥 Git is what gives a dev their power…It binds the galaxy together. Workspaces can currently support up to repositories for an Azure Project. Users can type either gk rebase -i or gk rebase —interactive along with two refs to open the interactive rebase view. If only one ref is passed it will perform the rebase of the branch currently checked out onto the specified ref. Bug Fixes: Bugs…You will never find a more wretched hive of scum and villainy. Users will see increased performance when opening a commit diff for very large images. Large images will now display as a binary file Instead of producing an error. For large files, such as images and other media, we recommend using Git LFS. Dotted graph lines will no longer take precedence when overlapping with solid lines in graph views. When un-hiding a remote, users can continue hiding or un-hiding remotes without waiting for the triggered automatic fetch to resolve. Azure DevOps integrations and all self hosted integrations will now work properly on our new Teams license tier. Users can now use quotation marks when naming Workspaces. All Organization and Team actions will remain available after using the login screen. The scrollbar in the GitKraken Terminal will now remain clickable in all situations. When a user pushes many files up at once to GitHub, they will no longer experience an OAuth infinite loop. Opening repositories via gitkraken —path when GitKraken is already open will now work as expected. Improvements: An elegant Git client for a more civilized age. Note: Significant work towards reducing checkout times for LFS repos is underway and we plan to include these improvements in the GitKraken Client v8. When creating a new Team, members can now be added as part of the creation process. Team members are now sorted by username in the Teams section, found in the left panel of GitKraken Client. Improvements to GitKraken Workspaces: Workspaces can now be shared as Team Workspaces, allowing users to share the Workspace with specific teams within their Organization. In the Workspaces Repository view, clicking on the name of a repository will open it in a Repo Tab. Users can view repository information by clicking on the Open Repository Details option, found on the right side of the Repositories view. Users will find more options for filtering in the Workspaces Pull Requests view. For Windows users, GitKraken Client will now respect the core. On Windows, core. GitKraken CLI autocomplete will now be able to suggest more than one argument in these commands: git add.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Download GitKraken crack (serial key) latest version XDR№

💾 ►►► DOWNLOAD FILE 🔥🔥🔥 Git is what gives a dev their power…It binds the galaxy together. Workspaces can currently support up to repositories for an Azure Project. Users can type either gk rebase -i or gk rebase —interactive along with two refs to open the interactive rebase view. If only one ref is passed it will perform the rebase of the branch currently checked out onto the specified ref. Bug Fixes: Bugs…You will never find a more wretched hive of scum and villainy. Users will see increased performance when opening a commit diff for very large images. Large images will now display as a binary file Instead of producing an error. For large files, such as images and other media, we recommend using Git LFS. Dotted graph lines will no longer take precedence when overlapping with solid lines in graph views. When un-hiding a remote, users can continue hiding or un-hiding remotes without waiting for the triggered automatic fetch to resolve. Azure DevOps integrations and all self hosted integrations will now work properly on our new Teams license tier. Users can now use quotation marks when naming Workspaces. All Organization and Team actions will remain available after using the login screen. The scrollbar in the GitKraken Terminal will now remain clickable in all situations. When a user pushes many files up at once to GitHub, they will no longer experience an OAuth infinite loop. Opening repositories via gitkraken —path when GitKraken is already open will now work as expected. Improvements: An elegant Git client for a more civilized age. Note: Significant work towards reducing checkout times for LFS repos is underway and we plan to include these improvements in the GitKraken Client v8. When creating a new Team, members can now be added as part of the creation process. Team members are now sorted by username in the Teams section, found in the left panel of GitKraken Client. Improvements to GitKraken Workspaces: Workspaces can now be shared as Team Workspaces, allowing users to share the Workspace with specific teams within their Organization. In the Workspaces Repository view, clicking on the name of a repository will open it in a Repo Tab. Users can view repository information by clicking on the Open Repository Details option, found on the right side of the Repositories view. Users will find more options for filtering in the Workspaces Pull Requests view. For Windows users, GitKraken Client will now respect the core. On Windows, core. GitKraken CLI autocomplete will now be able to suggest more than one argument in these commands: git add.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Azure Static Web Apps
Azure Static Web Apps is a service that automatically builds and deploys full stack web apps to Azure from a code repository.
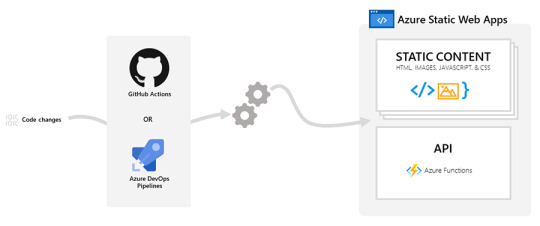
The workflow of Azure Static Web Apps is tailored to a developer's daily workflow. Apps are built and deployed based off code changes.
When you create an Azure Static Web Apps resource, Azure interacts directly with GitHub or Azure DevOps to monitor a branch of your choice. Every time you push commits or accept pull requests into the watched branch, a build is automatically run and your app and API is deployed to Azure.
Static web apps are commonly built using libraries and frameworks like Angular, React, Svelte, Vue, or Blazor where server side rendering is not required. These apps include HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image assets that make up the application. With a traditional web server, these assets are served from a single server alongside any required API endpoints.
With Static Web Apps, static assets are separated from a traditional web server and are instead served from points geographically distributed around the world. This distribution makes serving files much faster as files are physically closer to end users. In addition, API endpoints are hosted using a serverless architecture, which avoids the need for a full back-end server all together.
Key features
Web hosting for static content like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and images.
Integrated API support provided by Azure Functions with the option to link an existing Azure Functions app using a standard account.
First-class GitHub and Azure DevOps integration where repository changes trigger builds and deployments.
Globally distributed static content, putting content closer to your users.
Free SSL certificates, which are automatically renewed.
Custom domains to provide branded customizations to your app.
Seamless security model with a reverse-proxy when calling APIs, which requires no CORS configuration.
Authentication provider integrations with Azure Active Directory, GitHub, and Twitter.
Customizable authorization role definition and assignments.
Back-end routing rules enabling full control over the content and routes you serve.
Generated staging versions powered by pull requests enabling preview versions of your site before publishing.
What you can do with Static Web Apps
Build modern web applications with JavaScript frameworks and libraries like Angular, React, Svelte, Vue, or using Blazor to create WebAssembly applications, with an Azure Functions back-end.
Publish static sites with frameworks like Gatsby, Hugo, VuePress.
Deploy web applications with frameworks like Next.js and Nuxt.js.
Source : https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/static-web-apps/overview
Deploying Angular to Azure Static Web Apps
0 notes
Text
Choosing the Right Tools for Test Automation Framework

Choosing the Right Tools for Test Automation Framework Selecting the right tools is pivotal for the success of your test automation framework.
Here are key considerations and recommendations:
Technology Stack Compatibility Ensure the tool aligns with the technologies used in your application.
For example: Web Applications: Selenium, Cypress, Playwright. Mobile
Applications: Appium, Espresso, XCUITest.
API Testing: Postman, SoapUI, RestAssured.
If your stack involves multiple platforms (e.g., web, mobile, APIs), consider a hybrid tool like Katalon Studio.
2. Ease of Integration Choose tools that integrate seamlessly with your CI/CD pipeline and version control systems like Git.
Tools with plugins for Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Azure DevOps are highly recommended.
3. Community Support and Documentation Open-source tools like Selenium and Appium have large communities and abundant resources, making troubleshooting easier.
Commercial tools like TestComplete or Ranorex often come with robust customer support.
4. Budget Considerations Open-source tools (e.g., Selenium, Cypress) are cost-effective but require more customization. Licensed tools (e.g., TestComplete, Tosca) offer ready-made solutions and support but come at a higher cost.
5. Future-Readiness Opt for tools with AI/ML capabilities for predictive analytics and self-healing scripts, such as Testim or Tricentis Tosca. Cloud-based tools like BrowserStack and LambdaTest are excellent for scaling and remote testing.
Integrating CI/CD for Continuous Testing CI/CD integration ensures your test automation framework delivers fast feedback and supports continuous testing in agile environments.
Setting Up the Pipeline Use tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or CircleCI to create automated pipelines for build, test, and deployment.
Define stages in the pipeline:
Build: Compile the code and dependencies.
Test: Execute automated tests (unit, integration, functional). Deploy: Deploy to a staging or production environment.
2. Triggering Automated Tests Trigger test executions on specific events such as code commits, pull requests, or scheduled intervals.
Use webhooks or polling mechanisms to integrate the test framework with the CI/CD server.
3. Parallel and Cross-Browser Testing Configure parallel test execution to reduce overall runtime. Use tools like Selenium Grid, BrowserStack, or LambdaTest for cross-browser and cross-device compatibility testing.
4. Reporting and Notifications Integrate reporting tools like Allure, Extent Reports, or native CI/CD plugins for detailed test results. Configure notifications through Slack, Microsoft Teams, or email to alert teams about test outcomes.
5. Version Control Integration Store test scripts, test data, and configuration files in a version control system (e.g., Git). Use branching strategies (e.g., GitFlow) to manage test framework updates in sync with application development.
6. Scalability and Reliability Leverage containerization tools like Docker to create consistent test environments.
Use Kubernetes for managing test workloads at scale in large projects. By choosing the right tools and integrating CI/CD effectively, your test automation framework can deliver reliable, scalable, and efficient testing across the development lifecycle.

0 notes
Text
Data Factory ¿Que es? ¿Que NO es?
Hola a todos! En esta oportunidad quiero hablarles de mi servicio favorito (y probablemente de muchos otros Ingenieros de Datos) en Azure, que es Azure Data Factory. A modo de introducción, para hacer algo distinto se me ocurrió escribir sobre que es y que NO es Data Factory, ya que el servicio muchas veces es evaluado
Es un servicio que casi todo proyecto relacionado con analítica en Azure debería utilizar, salvando algunas muy raras excepciones. Provee muchísimas ventajas y simplifica un montón de aspectos clave para estos proyectos, como calendarización, orquestación, modularidad para procesos, entre otros. Pero también tiene (como todo servicio) sus limitaciones, que si bien son salvables de uno u otro modo, pueden llegar a dejar una mala impresión cuando recién nos iniciamos con la tecnología. El objetivo de este post es aclarar que ES Data Factory y que NO es, o que no hace por defecto (y posiblemente algún work-around para esas limitaciones).
¿Que es?
Empecemos por mencionar que es Data Factory, y porque es una herramienta casi imprescindible:
Pipelines!! Es simple agregar actividades (y dependencias entre ellas) como llevar datos de un storage a otro, buscar datos en bases de datos, condicionales, y todo tipo de estructuras de control.
Interfaz gráfica simple de entender, cualquiera que le dedique 10 minutos a ver la interfaz podrá entender y hacer algún pipeline básico para orquestar algún proceso.
Múltiples opciones de calendarización de pipelines gracias a los Triggers (disparadores), en función a eventos, ventanas de tiempo, según día, hora, numero de día. Por ej: el primer día de cada mes, todos los Miércoles, etc.
Parámetros: igual que en cualquier lenguaje de programación, podemos usar parámetros para alterar el funcionamiento de algunos componentes como Pipelines, Actividades, Datasets, etc. Pueden usarse básicamente en cualquier lugar donde haya un string, para evitar errores lo mejor es encapsular el llamado a parámetros en @{nombreParametro}. Nos permiten recorrer bases de datos enteras con 1 o 2 actividades.
Variables: podemos almacenar valores en variables para utilizarlos después, se asignan con la actividad de asignar variables y se llaman del mismo modo que los parámetros.
Modularidad en diseño: podemos "encapsular" ciertos procesos que vamos a repetir frecuentemente en un pipeline y después llamarlo desde otro pipe, mediante la actividad "Ejecutar pipeline", esto brinda mucha flexibilidad a la herramienta si agregamos el uso de parámetros y variables.
Serverless!! Nunca sabemos (ni nos importa) donde están los servidores que ejecutan los trabajos. Solo darle play al pipeline y Azure se encargara de manejar por nosotros la memoria, ancho de banda, procesador, etc. Hay algunas excepciones, como en el caso del Integration Runtime (que sera instalado en una pc/vm on premise) o los Mapping Dataflow (en los cuales elegimos el tamaño del cluster que sera provisto).
Alertas configurables para enterarnos inmediatamente cuando algo anda mal, con la opción de ser informados mediante Email, SMS, Push (notificación en el celular), o con un mensaje de voz. Esto se logra gracias a la integración con Azure Monitor.
Soporte para utilizar Polybase al mover datos entre un Data Lake o Blob Storage y Synapse, aprovechando la mejora en performance de esta tecnología.
Conexión con muchos servicios!! Mas de 80 conectores, literalmente se conecta a todo lo que este dentro de Azure, pero ademas puede interactuar con varios servicios de otras nubes como AWS (S3, Redshift, etc), recursos que se encuentren en redes on premise (requiere la instalación de un Integration Runtime) e incluso soporta Rest apis o conexiones ODBC, así que si un servicio no esta en el listado pero soporta esas formas de conexión, también sera posible conectarnos.
Múltiples tipos de archivos soportados: Json, Csv, Excel, ORC, Parquet, Avro, Binario (cualquier archivo, no sera interpretado el contenido).
Soporte para trabajar de forma cooperativa gracias a la integración con Git, se pueden usar repositorios en GitHub o Azure DevOps. Como todo su código son definiciones en Json, podemos enviar ese código a un repositorio y trabajarlo con una metodología similar a la de desarrollo convencional. Por ej: creamos nuestro propio branch, desarrollamos una feature, y una vez que esta todo testeado y funcionando, creamos un pull request a master.
Soporte para deploys automáticos, de modo que podemos tener entornos separados y asegurarnos que solo llegan a producción aquellas versiones de código que sabemos que funcionan bien.
Esas features mencionadas son excelentes! Ya podemos ver porque no imagino un proyecto de analítica ejecutado en Azure sin usar Data Factory.
¿Que NO es?
A pesar de todas las bondades del servicio, es notorio que cuando arrancamos a utilizarlo muchas personas esperan mas de el, y creo que es porque por todos lados lo muestran o publicitan como una "herramienta ETL", siendo que no lo es en un 100% (al menos en su versión básica). Por eso, para evitar malos entendidos y tener opciones para evaluar, acá va un listado de las cosas que NO es Data Factory (con sugerencias de solución):
NO es una herramienta de transformación de datos! Su principal objetivo es ser un orquestador, mantener servicios y procesos trabajando, moviendo los datos de un modo coordinado, con todas las ventajas nombradas anteriormente. Recientemente se añadió la posibilidad de hacer algunas transformaciones de datos gracias a sus dataflows (Wrangling y Mapping), pero aun así es una opción con mucho tiempo de startup, bastante costosa y mi recomendación es siempre utilizar algún servicio externo para hacer las transformaciones (puede ser Databricks, T-SQL en una base de datos o en Synapse, para algo sencillo Azure Functions o Automation).
NO maneja de forma automática las cargas incrementales! Esta es una consulta habitual que tengo entre los clientes. No es complicado de hacer, pero tampoco es tan straight-forward como muchos esperan (sobretodo si tienen experiencia previa con alguna herramienta ETL como StreamSets, Pentaho, Talend, NiFi, etc).
Por si solo NO prende o apaga servicios tales como Synapse, o Analysis Services. Para esto sera necesario escribir un pequeño script en PowerShell para ejecutar en Azure Automation o en uno de los múltiples lenguajes que soporta Azure Functions. Por supuesto que Data Factory si tiene capacidades para llamar a esos servicios y ejecutar el encendido o apagado de estos servicios. Cuando nos conectamos a Databricks, si tiene la capacidad de encender un job cluster, ejecutar un código y apagarlo.
Lo mismo sucede con el refresh de modelos en Azure Analysis Services, para estos sera necesario un script en alguno de los servicios mencionados previamente. Otra opción es disparar el refresco mediante la REST api del servicio.
Data Factory NO almacena datos (solo metadatos), de modo que si creamos un dataset para una tabla en una base de datos que tiene 1 millón de registros, ese dataset solo tendrá la forma de acceder a la base de datos (mediante su linked service), el nombre de la tabla, tipo de dato de cada columna, pero bajo ningún escenario contendrá todos los registros en Data Factory.
Entre actividades SOLO podemos intercambiar Metadata! Con la excepción de Lookup activity, que nos devolverá el resultado de una consulta como output de la actividad, que podremos consultar desde otras actividades o asignarlas a variables.
Seguro estoy olvidando algunas limitaciones o beneficios, pero a modo introductorio creo que estos son los puntos principales a tener en cuenta al momento de crearnos expectativas respecto a las capacidades del servicio.
Espero que les haya gustado, seguramente vendrán algunos artículos mas sobre el tema.
#azure#azure data factory#data factory#data engineering#azure argentina#azure cordoba#azure jujuy#azure tips
0 notes
Text
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger Azure devops pull request trigger Latest hot news Azure devops pull request trigger Trigger a build in Azure DevOps using Services hooks #10360 Comments Copy link Quote reply Naidul commented May 14, 2019 I am trying to queue a build in azure devops (VSTS) using Service Hooks. But I need to trigger a build in VSTS using Service hooks Please guide me joshmgross…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
A Guide to Automating Deployments Using Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions

A Guide to Automating Deployments Using Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions Automating deployments is a key aspect of modern software development, ensuring faster, reliable, and consistent delivery of applications.
Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions are two powerful tools that help streamline this process.
Here’s a brief guide:
Azure DevOps Pipelines Azure DevOps provides robust CI/CD pipelines for automating builds, tests, and deployments.
It supports various languages, platforms, and deployment targets.
Key steps include:
Define your pipeline:
Use YAML files (azure-pipelines.yml) to describe your build and release process.
Connect to deployment targets:
Integrate with cloud services like Azure, Kubernetes, or on-premises environments.
Use task-based automation: Leverage pre-built tasks for activities like building Docker images, running tests, and deploying to Azure App Service.
GitHub Actions GitHub Actions integrates seamlessly with GitHub repositories to automate workflows, including deployments.
Steps include:
Create a workflow file:
Define workflows in .github/workflows/ using YAML. Specify triggers: Automate workflows on events like commits or pull requests.
Define jobs and actions:
Use pre-built or custom actions to build, test, and deploy applications.
For instance, deploy to Azure using the official Azure Actions.
Key Benefits of Automation Efficiency:
Save time by automating repetitive tasks. Reliability: Reduce human error in deployment processes.
Scalability: Support complex pipelines for multi-environment and multi-cloud deployments.
By leveraging these tools, you can modernize your deployment processes, align with DevOps practices, and ensure high-quality delivery.
Whether you prefer the enterprise-grade features of Azure DevOps or the native GitHub ecosystem, both options provide the flexibility to build efficient CI/CD pipelines tailored to your needs.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/azure-data-factory-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
Digital transformation scenario with Azure, Visual Studio and Git
Scenario
How can you make a successful digital transformation in your company using Azure, Visual Studio, Git and other tools? What is your approach?
Acme is a successful accountancy firm based in the UK which is currently going through a digital transformation programme of work to modernise its legacy systems, using a proper approach for a real digital transformation scenario.
As part of the programme, Acme wants to become more “agile” and embrace new approaches and technology to deliver more modern and efficient services to its clients.
One of the key components of the transformation programme is an “Integration Platform” that will provide integration between core operational systems.
The Integration Platform will provide a scalable messaging layer that offers Acme the ability to decouple applications from each other such that, in the future, changing a system will not require the reimplementation of point-to-point services, but instead the fulfilment of a particular contract with the Integration Platform.
Landscape
As part of its digital transformation programme, Acme has adopted a cloud first strategy and Microsoft Azure is their chosen public cloud, integrated with Visual Studio and Git.
Acme’s small team of developers are relatively inexperienced in their approaches and in the past have typically only worked in isolation or in pairs to deliver projects with no formal process.
The developers have experience of using .NET Core and React and currently use Azure DevOps for managing their source code.
Architecture
The architecture of the Integration Platform is based around the Message Broker pattern using a “publish and subscribe” model to pass messages from one system (publisher) to another (subscriber).
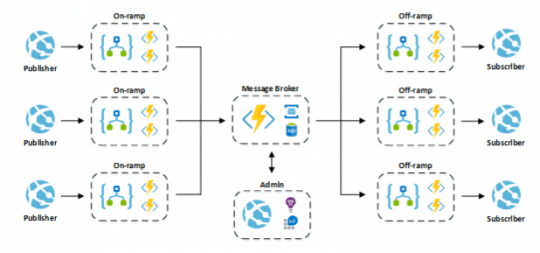
Architecture of the Integration Platform
Components
Component Description On-ramp A set of Azure logic apps and functions that are triggered by an event in a publisher system and send a message to the Message Broker. Message Broke An Azure function which is called by an on-ramp process and performs data transformation and enrichment operations on messages before placing them on an Azure service bus Off-ramp A set of Azure logic apps and functions that are triggered by a message being placed on an Azure service bus. Admin A web application providing administrative and monitoring capabilities for the Integration Platform. The application should be implemented using a React frontend with a .NET Core Web API backend.
Key requirements
The Architecture team have defined that the platform must use a “serverless” approach by default and use .NET Core for backend functions and APIs.
Each component should be independently testable and deployable.
Passwords and/or secrets for production systems must not be stored in source control or in plain text configuration settings.
Explain your view
Please describe how you would approach the delivery of Acme’s new integration platform in terms of your proposed:
approach to managing work items and / progress
structure of the source code repo(s) and what approach you would take to managing branches
approach to ensuring code quality is maintained and what tools/frameworks you would use
development toolset
approach to managing deployments including the required Azure resources
approach for managing passwords and secrets
Benefits to Acme of the approaches above
Any key risks or assumptions
Digital transformation scenario: what is your approach? My explanation
Proposed approach to managing work items and / progress
In the developer’s world, Agile methodology is the common way to manage the work and the workflow. Agile is a practice that promotes continuous iteration of development and testing throughout the software development lifecycle of the project.
Agile – Scrum
The architecture of Agile methodology is based on the same simple steps in a specific period of time. The time is usually 2 weeks and it is called Spring. The main steps are:
Sprint planning: the team estimates each user story and decide what tasks will be included in the next sprint.
Sprint: the period of time, usually 2 weeks, where the team is working on the tasks on the board
Daily Scrum Meet: every day, usually in the morning, the team is gathered and each person explains what he did the day before and the issues or blockers had faced
Sprint Review Meet is held at the end of the sprint to inspect the increment and adapt the product backlog if needed
Sprint Retrospective Meet: the team talks and analyses how the sprint went and highlighted what went well, wrong and could be improved. An easy free tool online is IdeaBoardz
Regularly, there is a grooming section separately where the team estimates the tickets, called Poker Plan (ie. planITpoker or PlanningPoker).

Agile methodology: anatomy of a sprint
During the sprint, the team has a board. For each user story, there are one or more tasks to complete. At the beginning of the sprint, all tasks are in the status of new.
So, each developer peeks up one ticket each time. When a developer picks up one ticket, he changes the status of the ticket to Active or In progress.
When the developer completes the task, he has to change the status in code completed. In some cases, the task can be moved in the Resolved status.
The ticket is now ready for the testers. Testers are responsible to check the functionalities and if the acceptance criteria are satisfied.
Then, the task is completed and it is possible to close it and change its status to Complete.
This process has simple steps. Every company can organize the process and the label of this process as it is more convenient.
Microsoft Azure DevOps
As developers, Azure DevOps offers a good integrated platform to manage the Agile ceremony.
Therefore, other tools are more business oriented like Jira. In a digital transformation scenario this are important tools to define at the beginning of your approach.
Important note is Azure DevOps is integrated in Visual Studio and it is also possible to browse you Git repository.

An example of spring board in Azure DevOps
Discriminating Epics, Features and User stories
After that, it is difficult to understand the different among these 3 parts of the process. Apparently, epics, features and user stories are all forms of expressing user need and implied benefit, but at different level of abstraction.
While there is no rigorous way to determine whether a “think you know you want to do” is an epic, feature and user story, the following table of discriminators should help:
Type of information Description Responsibility Time frame & Sizing Expression format Testable Strategic Product Theme BIG, hairy, audacious, game changing, initiatives. Differentiating, and providing competitive advantage. Portfolio fiduciaries San strategic planning horizon, 12-28+ months. Not sized, controlled by percentage investment Any: text, prototype, PPT, video, conversation No Epic Bold, impactful, marketable differentiators Program and product management, business owners 6-12 months. Sized. Most any, including prototype, mockup, declarative form or user story canonical form No Feature Short, descriptive, value delivery and benefit oriented statement. Customer and marketing understandable. Product Manager and Product Owner Fits in an internal release, divide into incremental sub-features as necessary. Sized in points. Declarative form or user story canonical form. May be elaborated with system use cases. Yes User story Small atomic. Fit for team and detailed user understanding Product Owner and Team Fits in a single iteraion. Sized in story points. User story canonical form Yes

Epics are the highest-level requirements artefact
Proposed structure of the source code repo(s) and what approach you would take to managing branches
As a developer, I like to have an integrate environment for repositories, deployment and resources such as web app and/or server less applications.
For this reason, I’m using Azure DevOps: it is free for unlimited repositories but max 5 users.
For each repository, I’m following a common structure that allows you to manage the master branch, a developer branch, tagged releases and hot fixes. This is Gitflow.
In our repository’s structure you have some main folders:
feature: for creating new tasks
bug: fix some exists functionalities
hotfix: fix some bugs in production
In the configuration of the CD/CI, there is a peer to peer review for merging a branch to the develop branch or master.
When a new branch is merged in the develop branch, the CD/CI process, automatically prepare the build and start the deployment.
In Agile point of view, each developer is responsible for a single task at the time. For this task, the developer has to create a branch. Common practice is naming each branch with the task number and a short description in the right folder. For example
feature/511-Login
When a developer completes a task has to create a new Pull Request to merge his changes to the develop branch. If the developers finished the peer to peer review, the branch is merged on develop.
For admin purposes, each branch could be associated with a task in the board. So, when a branch is merged, the correspond task is closed.
Every developer can manage this Git flow in the Azure DevOps and also directly in Visual Studio.
Proposed approach to ensuring code quality is maintained and what tools/frameworks you would use
As developer, you know you have to learn constantly: every day new technologies come up, new tools, new environments. The interaction between developers is important because we can teach each other something new. Also, developers (and no developers) can use Visual Studio to browse the dashboard in Azure DevOps and Git repositories.
For this reason, show your code to other developers is always a good way to improve the quality of your code and at the same time to learn something new. Nonetheless, websites like Github are so popular with a lot of users. In your team, peer-to-peer review is the simple way to check your code and find new implementation or structures. To be on the same page, a weekly meeting to share information should have an important impact in your team.
In Visual Studio, Code Analysis is an integrate tools. The Code Analysis feature of Visual Studio performs static code analysis to help developers identify potential design, globalization, interoperability, performance, security, and a host of other categories of potential problems.
You can run Code Analysis manually at any time from within the Visual Studio IDE, or even setup to automatically run as part of check-in policy for Azure DevOps Server.
Linters and Code Analysis
GCop is a fairly new set of C# code analysis rules (with really nice setup, use and rules documentation) from Geeks Ltd., which may be worth checking out if you’re not entirely satisfied with other code analysis rulesets (or perhaps using alongside of those other rules for extended coverage).
GCop is intended to be installed in your project as a NuGet package. To allow for rules that can’t run from a package, Paymon has released a GCop.Extra Visual Studio 2017 extension for use with GCop.
The extension enables GCop rules such as Minimum Scope that detect whether methods that are more visible than they need to be.
MultiLinter
MultiLinter, by Giovanni Lambiase, enables you to replace the (already outdated) linters built into Visual Studio 2017 with the standard linters available through Node.js including (but not limited to) ESLint, JSLint, JSHint, Stylelint, CssLint and Sass-lint.
MultiLinter lets you turn verbose debugging on, configure which linters to use (including running multiple linters against a file at the same time), update linters and linting rules, set rule severity warnings, and much more.
XamRight
XamRight, from Critical Hit Tech, is an extension for Visual Studio 2015 and 2017 that brings design-time code analysis and coding assistance to Xamarin.Forms XAML development.
You get IntelliSense, warnings, view model and data binding analysis and debugging, navigation tools for moving between XAML and C# model definitions, custom view implementations and more, along with navigation from XAML resource references to definitions.
XamRight can analyze your own model-view model binding, but also includes built-in support for popular MVVM frameworks including MVVMCross, MVVMLight, FreshMVVM, Prism and Caliburn.Micro.
A 30-day free trial is available and licensing is available on a monthly or yearly basis.
NDepend
NDepend, one of the most popular commercial static code analysis tools for .NET Framework development, recently released a substantial update including support for .NET Core 2.1, ubiquitous language checks in Domain Driven Design (DDD), performance improvements for Visual Studio 2017 and over a dozen new or improved code analysis rules.
A key new feature for NDepend is real-time technical debt estimation that’s updated as you code. Proud of that new method? Guess what, you just added 30 minutes of future technical debt. Maybe check NDepend’s analysis and spend a minute refactoring. I love it. NDepend offers a free 14-day trial and per-developer or per-build machine licensing.

NDepend’s Static Analysis Tools Have Been Updated for .NET Core 2
Async Method Name Fixer is an effective little tool for doing a simple but often overlooked task: making sure your async methods are named appropriately.
In a nutshell, it looks for methods defined as async and, if you haven’t given the method a name with “Async” on the end, the extension flags all instances of the method and calls to it.
Code Coverage and Testing
AxoCover, by axodox (Péter Major), provides Visual Studio integration for code coverage and unit testing with OpenCover. AxoCover lets you run, debug and check code coverage for unit tests in .NET Framework projects for Windows.
You can browse and analyse coverage by test in a hierarchical view and dig down into line-by-line coverage and test results. AxoCover supports the MSTest, xUnit and NUnit test frameworks.
SmartTests.Extension
SmartTests Extension, by Ludovic Dubois, is an extension to show current and missing tests for NUnit, Xunit and MSTest within Visual Studio.
SmartTests integrates into your Visual Studio environment the Pretty Objects SmartTests library, which helps you write smart unit tests, and the SmartTests.Analyzer, a Roslyn Analyzer to display missing tests as warnings.
The extension shows tests in a centralized window, lets you see current tests and any missing tests, and lets you navigate quickly to specific tests.
TestLeft
SmartBear’s TestLeft UI test automation framework supports Visual Studio 2013, 2015 and 2017. TestLeft integrates directly into the Visual Studio development environment, enabling you to create tests as you code.
A built-in object spy gives you the ability to create tests that support over 500 common Web and desktop UI controls.
You can create automated tests for a variety of popular development frameworks including .NET Framework, Winforms, WPF, Java, HTML5 and AngularJS.
Further test coverage includes controls from Infragistics, DevExpress, Syncfusion and Telerik, along with cross-browser testing with legacy versions of Internet Explorer, Edge, Firefox and Chrome.
Tests created in TestLeft can be migrated into TestComplete for automated testing as part of your continuous integration and release management processes.
Register online for a free 30-day trial. Yearly per-node and floating licenses are available from SmartBear.

TestLeft Simplifies the Creation of UI Test Automation as You Code
Selenium
Selenium is an umbrella project for a range of tools and libraries that enable and support the automation of web browsers.
It provides extensions to emulate user interaction with browsers, a distribution server for scaling browser allocation, and the infrastructure for implementations of the W3C WebDriver specification that lets you write interchangeable code for all major web browsers.
Selenium is made possible by volunteer contributors who have put in thousands of hours of their own time, and made the source code freely available for anyone to use, enjoy, and improve.
Testing with BDD
Digital transformation could drive you to change approach on testing.
Behavior Driven Development (BDD) is an agile software development practice – introduced by Dan North in 2006 – that encourages collaboration between everyone involved in developing software.
So, developers, testers, and business representatives such as product owners or business analysts.
In other words, BDD aims to create a shared understanding of how an application should behave by discovering new features based on concrete examples. Key examples are then formalized with natural language following a Given/When/Then structure.
SpecFlow
Gherkin is the most commonly used syntax for describing examples with Given/When/Then in plain text files, called feature files.
Gherkin scenarios can be automated to validate the expected behavior. At this point, BDD tools – such as SpecFlow – come in handy. Automated acceptance tests, however, are an optional by-product of using BDD, not the sole purpose.
SpecFlow is the #1 .NET open source framework for Behavior Driven Development, Acceptance Test Driven Development and Specification by Example.
In SpecFlow, specifications are written in plain, simple language which is defined by the Gherkin Syntax (Given-When-Then).

Gherkin scenario
SpecFlow provides a whole ecosystem of tools to use BDD on Azure DevOps and the Microsoft .NET platform. Besides SpecFlow and SpecFlow+Runner, there is also a SpecFlow Visual Studio Extension that provides a Gherkin editor and build integration.
SpecMap and SpecFlow+LivingDoc are Azure DevOps extensions that support the team in the overall BDD process with managing their backlog using story maps and accessing their living documentation.

SpecFlow architecture
Better Debugging
Angel Hernandez’s VisualSOS.Extension gives you access to features of the Microsoft SOS Debugging Extension and Windbg that are not available directly from the Visual Studio Debugger.
VisualSOS.Extension also gives you menu access to those features instead of having to remember the commands and option flags. Visual SOS is available as both a Visual Studio 2017 extension and a stand-alone debugger.
To learn more, see Hernandez’s blog post Visual SOS – Visual Studio extension to debug managed applications through SOS for an overview and some tips for more effective debugging with SOS.
VisualSOS Adds SOS and WinDbg Debugging Tools to Visual Studio
LINQBridgeVs
LINQBridgeVs, from Coding Adventures, provides a Custom Debugger Visualizer within Visual Studio that creates a bridge between your Visual Studio debugging session and the external LINQPad scratchpad and test environment.
After rebuilding your project, you can right-click on any public classes or structs in the project and open the related debugging data within LINQPad.
Microsoft Visual Studio Live Share
Microsoft’s Visual Studio Live Share, provides a collaborative development environment, enabling you to share code, collaboratively edit, securely share local servers and even collaboratively debug your code in real-time.
It’s not a screen share service or centralized codebase; you’re able to work independently in your local Visual Studio environment while collaborating on code editing and debugging.
As we go to press, the VS Live Share is in limited preview: anyone can download the extension, run it and join a session, but permission to share a session requires registration and acceptance into the preview.
For more details about VS Live Share including demos, see the Visual Studio Live Share Web site and Visual Studio Live Share Microsoft Docs.
Finally, the integration among Azure DevOps, Git and Visual Studio allows developers to use only one tools for coding and manage branches and share code and knowledge.
Proposed development toolset
Visual Studio is the main tool for developer and Microsoft releases it in different flavour:
Community: basic functionalities for developers for creating desktop application, web applications, mobile applications, libraries and much more with .NET and other languages.
Professional: more tools dev oriented for debugging, integration and team interconnection
Enterprise: developer’s dream, everything is here
Visual Studio Core: editing and debugging on any OS in a simplify environment
Visual Studio for Mac: develop apps and games for iOS, Android, and web using .NET (Xamarin)
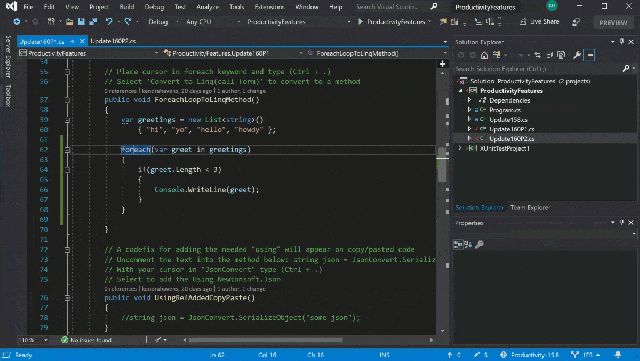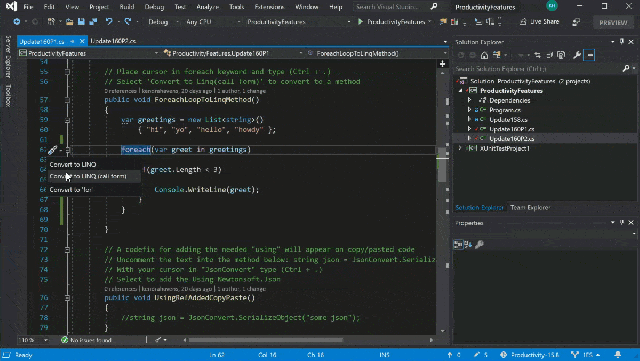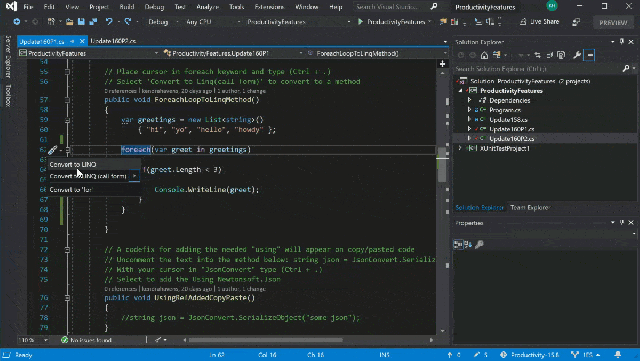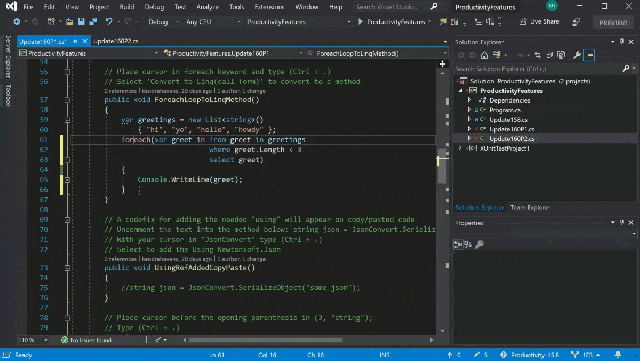
Visual Studio in action
Most important, Visual Studio is really cloud oriented: there is a total integration with Azure, the Microsoft Cloud, and Git. You can explore all Azure resources directly from your Visual Studio.
Microsoft Azure, the cloud
Azure is the Microsoft Cloud. You can deploy every kind of applications built with any languages, not only .NET: it is a very friendly environment and easy to use, in the usual Microsoft style.
In Azure you can create different subscription (you can think a subscription as an environment, for example a subscription for test, another for stage and another for production).
Under each subscription there are one or more resource group: a resource group is a collection of Azure services such as web applications, Azure functions, LogicApp, service bus and much more.
There are some tools to explore better some Azure resources:
Service Bus Explorer: the Service Bus Explorer allows users to connect to a Service Bus namespace and administer messaging entities in an easy manner. The tool provides advanced features like import/export functionality or the ability to test topic, queues, subscriptions, relay services, notification hubs and events hubs. Source code on Github.
Azure Media Services Explorer (AMSE) is a Winforms/C# application for Windows that does upload, download, encode and stream VOD and live content with Azure Media Services v3. Source code on Github
Azure Storage Explorer: easily manage the contents of your storage account with Azure Storage Explorer. Upload, download, and manage blobs, files, queues, tables, and Cosmos DB entities. Gain easy access to manage your virtual machine disks. Work with either Azure Resource Manager or classic storage accounts, plus manage and configure cross-origin resource sharing
Now, Azure Functions and Logic Apps are very popular in the Microsoft world. Both developers and non-developers can create very complex workflows with few clicks.
Gitflow
I said I propose to use Gitflow to manage branches. There are a lot of tools for that. Also, Visual Studio has one and you can install it from the Visual Studio Installer but this has very basic functionalities. I recommend one of the following tools:
Sourcetree simplifies how you interact with your Git repositories so you can focus on coding. Visualize and manage your repositories through Sourcetree’s simple Git GUI. This tool is free
Gitkraken is very simple and the look is quite pretty. For free, you have better functionalities than Visual Studio and it is easy to manage your branches. There is an extension for Gitflow but only for the version with licence.
Mobile environment
Generally speaking, if you want to create apps for iOS and Android, I really recommend to have some physical devices. Android is the tricky one because it supports a lot of different devices with different screen sizes.
Therefore, if you want to create apps for the iOS world, you must have a Mac to compile and test your application.
Deploy and test an application on a Simulator is free but if you want to test your application on a real device, you must pay the fee as developer to Apple.
To build and distribute your app, you can use Microsoft AppCenter: it is simple to use, efficient and it collects the data of usage and crashes for you in a simple interface.
In Visual Studio you have a perfect integration of mobile with Xamarin but also with Azure DevOps and Git repositories.
Proposed approach to managing deployments including the required Azure resources
I mentioned before Gitflow that you can use to manage your repositories in Azure DevOps. Also, DevOps allows you to create pipelines to deploy your projects directly into your cloud resources such as web application, Logic Apps, Azure Functions and so on.
For example, you can create a pipeline based on events. For example, when a branch is merged in develop branch, DevOps automatically starts the build and the deployment. There is a document on Microsoft to How to create your first pipeline in Azure DevOps.
youtube
With Azure Pipelines you can build and deploy your code written in any language using any platform, no problem. In this video we will show why Azure Pipelines is the best tool on the planet for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) of your code.
The developers can create every resource in Azure via an ARM script. I discussed that in another post on this blog. So, during the deployment, Azure DevOps is also able to generate the environment before deploying your projects. You can write your ARM scripts or use the template and script generator in the Azure Portal.
In Visual Studio, developers can create the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) script, save in a Git repository and deploy everything in the company environment.
Proposed approach for managing passwords and secrets
A common approach to manage password was to create a sealed class in C# where they store all password. Very insecure way to protect your password for your environment. Another approach is the create app.settings for different environments but again this is not secure at all.
In Azure for resources like web application and Azure functions, there is a Configuration section. If you add your configuration for a specific environment, Azure rewrites the settings in the application with these values. Only if you have access to this resource in Azure, you can see the real values.
For instance, if you are using Azure DevOps, the pipeline has a parameter section where you put the settings based on the environment. So, when DevOps is building your project, it uses the proper configuration for the environment.
The most secure way to store your password is Azure KeyVault. Create a KeyVault in Azure is pretty simple but the protection KeyVault offers is very high. Every application has only a name and a client key to access to your KeyVault and the real password or certificate or secrets won’t never revealed.
It is easy to integrate Azure KeyVault with Visual Studio in your project and also publish your code, in a safe way, in your Git repositories without exposing your credentials.
Benefits to Acme of the approaches above
What I describe in this post is based on my experience in several companies and also, I ran my own company for more than 15 years. I saw and used this approach and I guarantee that our team can have a very positive benefit introducing this your new approach for the digital transformation.
Your team and your company could face at the beginning a couple of weeks of assessment because you have to understand how to implement these new changes and use new tools but it is worth.
All companies are using or going to use a similar approach: it is very common, there are a lot of tutorial and how to that you can read and follow and even books. Also, there are a lot of consultants and specialists can help you to adopt new behaviours to digital transform your company in better.
In addition, in developers’ point of view, there is a great integration using Visual Studio with Azure and Git repositories (Git is now a Microsoft product). Then your team has a consistent environment for desktop applications, mobile applications, web applications and cloud tools.
Any key risks or assumptions
Change the direction of a company is always a challenge. It is a good opportunity to involve people in something new, show to your team the company wants innovate because people are really the heart of your company.
As usual, at the beginning could be harsh because you have to introduce new tools and new behaviour. After a couple of months, you and your company will see the result, how the productivity is increased and people happy.
In addition, it is important to underline again, the integrating environment your company can use with Visual Studio, Azure, Git and other tools like Xamarin.
Human risk is the big factor in this scenario because sometimes people don’t want to change, in particular if they are in the company for as long time and they have their habit.
In conclusion, a digital transformation allows the company to be competitive and share common values with clients and other competitors.
The post Digital transformation scenario with Azure, Visual Studio and Git appeared first on PureSourceCode.
from WordPress https://www.puresourcecode.com/dotnet/digital-transformation-scenario-azure-visual-studio-git/
0 notes
Text
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger Azure devops pull request trigger Daily news Azure devops pull request trigger Azure DevOps Pull Request Templates Devguides Read more posts by this author. Devguides Pull requests are a very handy feature when you are working in a team. However, you might want to have a check list of some sort or maybe a special format on your pull requests. One way to…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger
Azure devops pull request trigger Azure devops pull request trigger World news Azure devops pull request trigger Pull Request Builds in Azure DevOps Picking up from where I left in the previous note… the other part of the request was to add a conditional step in the associated build definition and update the release definition accordingly. I will elaborate on that here. Our typical code cycle…

View On WordPress
0 notes